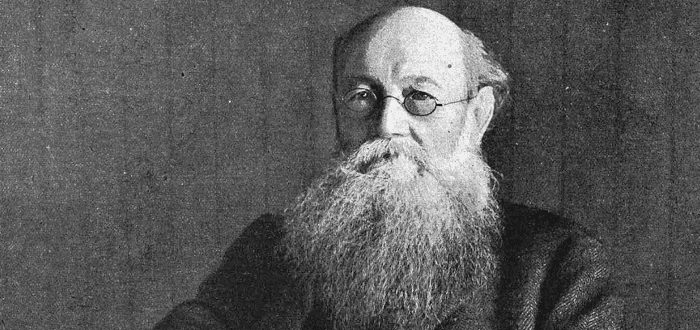Peter Kropotkin was a Russian naturalist and anarchist born into an aristocratic Russian family in 1842. In this passage from his classic work Mutual Aid: A Factor of Evolution, Kropotkin argues against a narrow reading of Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution promoted by Social Darwinists such as T. H. Huxley and Herbert Spencer. Huxley and Spencer saw the process of evolution as a cutthroat struggle of every individual against all others in which only the strongest survive. They argued that this principle of mutual struggle applies not just to animals and the natural world but also to human societies.
Kropotkin, drawing upon his extensive observations of Siberian ecosystems, argues that while mutual struggle is a factor in evolution, mutual aid is at least as important in nature and is especially important in human evolution. He argues that this mutual aid instinct, and the social institutions that foster and promote mutual aid, are crucial to a well-functioning society and that the growing dominance of state and capitalist institutions in Western European countries promotes a kind of egoistic individualism that threatens these mutual aid institutions and therefore the well-being of society. Kropotkin advocates for a society built around this notion of mutual aid rather than one built around a Hobbesian or Social Darwinist conception of society in which an ever-present threat of the “war of all against all” is present if political institutions were to break down.
Reading
[The following reading is from chapters 1, 7, and 8 of Kropotkin’s Mutual Aid. The full text can be found online here.]
The conception of struggle for existence as a factor of evolution, introduced into science by Darwin and Wallace, has permitted us to embrace an immensely wide range of phenomena in one single generalization, which soon became the very basis of our philosophical, biological, and sociological speculations. An immense variety of facts:— adaptations of function and structure of organic beings to their surroundings; physiological and anatomical evolution; intellectual progress, and moral development itself, which we formerly used to explain by so many different causes, were embodied by Darwin in one general conception. … [Darwin] foresaw that the term which he was introducing into science would lose its philosophical and its only true meaning if it were to be used in its narrow sense only — that of a struggle between separate individuals for the sheer means of existence. And at the very beginning of his memorable work he insisted upon the term being taken in its “large and metaphorical sense including dependence of one being on another, and including (which is more important) not only the life of the individual, but success in leaving progeny.”
While he himself was chiefly using the term in its narrow sense for his own special purpose, he warned his followers against committing the error (which he seems once to have committed himself) of overrating its narrow meaning. In The Descent of Man he gave some powerful pages to illustrate its proper, wide sense. He pointed out how, in numberless animal societies, the struggle between separate individuals for the means of existence disappears, how struggle is replaced by cooperation, and how that substitution results in the development of intellectual and moral faculties which secure to the species the best conditions for survival. He intimated that in such cases the fittest are not the physically strongest, nor the cunningest, but those who learn to combine so as mutually to support each other, strong and weak alike, for the welfare of the community. “Those communities,” he wrote, “which included the greatest number of the most sympathetic members would flourish best, and rear the greatest number of offspring” (2nd edit., p. 163). The term, which originated from the narrow Malthusian conception of competition between each and all, thus lost its narrowness in the mind of one who knew Nature.
…
It happened with Darwin’s theory as it always happens with theories having any bearing upon human relations. Instead of widening it according to his own hints, his followers narrowed it still more. … They came to conceive the animal world as a world of perpetual struggle among half-starved individuals, thirsting for one another’s blood. They made modern literature resound with the war-cry of woe to the vanquished, as if it were the last word of modern biology. They raised the “pitiless” struggle for personal advantages to the height of a biological principle which man must submit to as well, under the menace of otherwise succumbing in a world based upon mutual extermination.
…
In how far this view of nature is supported by fact, will be seen from the evidence which will be here submitted to the reader as regards the animal world, and as regards primitive man. But it may be remarked at once that Huxley’s [Social Darwinist] view of nature had as little claim to be taken as a scientific deduction as the opposite view of Rousseau, who saw in nature but love, peace, and harmony destroyed by the accession of man. In fact, the first walk in the forest, the first observation upon any animal society, or even the perusal of any serious work dealing with animal life (D’Orbigny’s, Audubon’s, Le Vaillant’s, no matter which), cannot but set the naturalist thinking about the part taken by social life in the life of animals, and prevent him from seeing in Nature nothing but a field of slaughter, just as this would prevent him from seeing in Nature nothing but harmony and peace. Rousseau had committed the error of excluding the beak-and-claw fight from his thoughts; and Huxley committed the opposite error; but neither Rousseau’s optimism nor Huxley’s pessimism can be accepted as an impartial interpretation of nature.
As soon as we study animals — not in laboratories and museums only, but in the forest and the prairie, in the steppe and the mountains — we at once perceive that though there is an immense amount of warfare and extermination going on amidst various species, and especially amidst various classes of animals, there is, at the same time, as much, or perhaps even more, of mutual support, mutual aid, and mutual defence amidst animals belonging to the same species or, at least, to the same society. Sociability is as much a law of nature as mutual struggle. Of course it would be extremely difficult to estimate, however roughly, the relative numerical importance of both these series of facts. But if we resort to an indirect test, and ask Nature: “Who are the fittest: those who are continually at war with each other, or those who support one another?” we at once see that those animals which acquire habits of mutual aid are undoubtedly the fittest. They have more chances to survive, and they attain, in their respective classes, the highest development of intelligence and bodily organization. If the numberless facts which can be brought forward to support this view are taken into account, we may safely say that mutual aid is as much a law of animal life as mutual struggle, but that, as a factor of evolution, it most probably has a far greater importance, inasmuch as it favours the development of such habits and characters as insure the maintenance and further development of the species, together with the greatest amount of welfare and enjoyment of life for the individual, with the least waste of energy.
…
[Chapters 1 through 6 of Mutual Aid outline various forms of mutual aid in nature, as well as among “savages”, “barbarians”, and in medieval cities.]
The mutual-aid tendency in man has so remote an origin, and is so deeply interwoven with all the past evolution of the human race, that it has been maintained by mankind up to the present time, notwithstanding all vicissitudes of history. It was chiefly evolved during periods of peace and prosperity; but when even the greatest calamities befell men — when whole countries were laid waste by wars, and whole populations were decimated by misery, or groaned under the yoke of tyranny — the same tendency continued to live in the villages and among the poorer classes in the towns; it still kept them together, and in the long run it reacted even upon those ruling, fighting, and devastating minorities which dismissed it as sentimental nonsense. And whenever mankind had to work out a new social organization, adapted to a new phasis of development, its constructive genius always drew the elements and the inspiration for the new departure from that same ever-living tendency. New economical and social institutions, in so far as they were a creation of the masses, new ethical systems, and new religions, all have originated from the same source, and the ethical progress of our race, viewed in its broad lines, appears as a gradual extension of the mutual-aid principles from the tribe to always larger and larger agglomerations, so as to finally embrace one day the whole of mankind, without respect to its divers creeds, languages, and races.
…
For … three centuries, the [European] States, both on the Continent and in these islands, systematically weeded out all institutions in which the mutual-aid tendency had formerly found its expression. The village communities were bereft of their folkmotes, their courts and independent administration; their lands were confiscated. The guilds were spoliated of their possessions and liberties, and placed under the control, the fancy, and the bribery of the State’s official. The cities were divested of their sovereignty, and the very springs of their inner life — the folkmote, the elected justices and administration, the sovereign parish and the sovereign guild — were annihilated; the State’s functionary took possession of every link of what formerly was an organic whole. Under that fatal policy and the wars it engendered, whole regions, once populous and wealthy, were laid bare; rich cities became insignificant boroughs; the very roads which connected them with other cities became impracticable. Industry, art, and knowledge fell into decay. Political education, science, and law were rendered subservient to the idea of State centralization. It was taught in the Universities and from the pulpit that the institutions in which men formerly used to embody their needs of mutual support could not be tolerated in a properly organized State; that the State alone could represent the bonds of union between its subjects; that federalism and “particularism” were the enemies of progress, and the State was the only proper initiator of further development. By the end of the last century the kings on the Continent, the Parliament in these isles, and the revolutionary Convention in France, although they were at war with each other, agreed in asserting that no separate unions between citizens must exist within the State; that hard labour and death were the only suitable punishments to workers who dared to enter into “coalitions.” “No state within the State!” The State alone, and the State’s Church, must take care of matters of general interest, while the subjects must represent loose aggregations of individuals, connected by no particular bonds, bound to appeal to the Government each time that they feel a common need. Up to the middle of this century this was the theory and practice in Europe. Even commercial and industrial societies were looked at with suspicion. As to the workers, their unions were treated as unlawful almost within our own lifetime in this country and within the last twenty years on the Continent. The whole system of our State education was such that up to the present time, even in this country, a notable portion of society would treat as a revolutionary measure the concession of such rights as every one, freeman or serf, exercised five hundred years ago in the village folkmote, the guild, the parish, and the city.
The absorption of all social functions by the State necessarily favoured the development of an unbridled, narrow-minded individualism. In proportion as the obligations towards the State grew in numbers the citizens were evidently relieved from their obligations towards each other. In the guild — and in medieval times every man belonged to some guild or fraternity two “brothers” were bound to watch in turns a brother who had fallen ill; it would be sufficient now to give one’s neighbour the address of the next paupers’ hospital. In barbarian society, to assist at a fight between two men, arisen from a quarrel, and not to prevent it from taking a fatal issue, meant to be oneself treated as a murderer; but under the theory of the all-protecting State the bystander need not intrude: it is the policeman’s business to interfere, or not. And while in a savage land, among the Hottentots, it would be scandalous to eat without having loudly called out thrice whether there is not somebody wanting to share the food, all that a respectable citizen has to do now is to pay the poor tax and to let the starving starve. The result is, that the theory which maintains that men can, and must, seek their own happiness in a disregard of other people’s wants is now triumphant all round in law, in science, in religion. It is the religion of the day, and to doubt of its efficacy is to be a dangerous Utopian. Science loudly proclaims that the struggle of each against all is the leading principle of nature, and of human societies as well. To that struggle Biology ascribes the progressive evolution of the animal world. History takes the same line of argument; and political economists, in their naive ignorance, trace all progress of modern industry and machinery to the “wonderful” effects of the same principle. The very religion of the pulpit is a religion of individualism, slightly mitigated by more or less charitable relations to one’s neighbours, chiefly on Sundays. “Practical” men and theorists, men of science and religious preachers, lawyers and politicians, all agree upon one thing — that individualism may be more or less softened in its harshest effects by charity, but that it is the only secure basis for the maintenance of society and its ulterior progress.
It seems, therefore, hopeless to look for mutual-aid institutions and practices in modern society. What could remain of them? And yet, as soon as we try to ascertain how the millions of human beings live, and begin to study their everyday relations, we are struck with the immense part which the mutual-aid and mutual-support principles play even now-a-days in human life. Although the destruction of mutual-aid institutions has been going on in practice and theory, for full three or four hundred years, hundreds of millions of men continue to live under such institutions; they piously maintain them and endeavour to reconstitute them where they have ceased to exist. In our mutual relations every one of us has his moments of revolt against the fashionable individualistic creed of the day, and actions in which men are guided by their mutual aid inclinations constitute so great a part of our daily intercourse that if a stop to such actions could be put all further ethical progress would be stopped at once. Human society itself could not be maintained for even so much as the lifetime of one single generation. These facts, mostly neglected by sociologists and yet of the first importance for the life and further elevation of mankind, we are now going to analyze, beginning with the standing institutions of mutual support, and passing next to those acts of mutual aid which have their origin in personal or social sympathies.
[Kropotkin goes on to list a wide array of contemporary mutual aid institutions from various countries.]
For every one who has any idea of the life of the labouring classes it is evident that without mutual aid being practised among them on a large scale they never could pull through all their difficulties. It is only by chance that a worker’s family can live its lifetime without having to face such circumstances as the crisis described by the ribbon weaver, Joseph Gutteridge, in his autobiography. And if all do not go to the ground in such cases, they owe it to mutual help. In Gutteridge’s case it was an old nurse, miserably poor herself, who turned up at the moment when the family was slipping towards a final catastrophe, and brought in some bread, coal, and bedding, which she had obtained on credit. In other cases, it will be some one else, or the neighbours will take steps to save the family. But without some aid from other poor, how many more would be brought every year to irreparable ruin!
…
In short, neither the crushing powers of the centralized State nor the teachings of mutual hatred and pitiless struggle which came, adorned with the attributes of science, from obliging philosophers and sociologists, could weed out the feeling of human solidarity, deeply lodged in men’s understanding and heart, because it has been nurtured by all our preceding evolution. What was the outcome of evolution since its earliest stages cannot be overpowered by one of the aspects of that same evolution. And the need of mutual aid and support which had lately taken refuge in the narrow circle of the family, or the slum neighbours, in the village, or the secret union of workers, re-asserts itself again, even in our modern society, and claims its rights to be, as it always has been, the chief leader towards further progress. Such are the conclusions which we are necessarily brought to when we carefully ponder over each of the groups of facts briefly enumerated in the last two chapters.
Further reading
- Read the full text of Mutual Aid here
- Find a few introductory resources on Anarchism here
- Check out a list of the best philosophy books on Anarchism here
- View a selection of university course syllabi on Anarchism here
The Daily Idea aims to make learning about philosophy as easy as possible by bringing together the best philosophy resources from across the internet. To get started, check out this organized collection of 400+ articles, podcasts, and videos on a wide range of philosophical topics.
A Collection of the Greatest Philosophical Quotations
A History of Western Philosophy in 500 Essential Quotations is a collection of the greatest thoughts from history’s greatest thinkers. Featuring classic quotations by Aristotle, Epicurus, David Hume, Friedrich Nietzsche, Bertrand Russell, Michel Foucault, and many more, A History of Western Philosophy in 500 Essential Quotations is ideal for anyone looking to quickly understand the fundamental ideas that have shaped the modern world.